
PNG vs JPG: Which Format Should You Use?
Choosing between PNG and JPG depends on your image needs. PNG offers lossless compression and supports transparency, making it ideal for graphics, logos, and text-based visuals. JPG, on the other hand, uses lossy compression, resulting in smaller file sizes, making it better for photographs and web content where speed and storage matter.
Key Differences:
- PNG: Preserves all image details, supports transparency, larger file sizes.
- JPG: Compresses data for smaller files, no transparency, may lose quality after edits.
Quick Comparison:
| Feature | PNG | JPG |
|---|---|---|
| Compression Type | Lossless | Lossy |
| Transparency | Yes | No |
| File Size | Larger | Smaller |
| Best For | Graphics, logos, text | Photos, web content |
| Editing Quality | Maintains quality | Degrades with saves |
For photos, go with JPG. For graphics requiring sharpness or transparency, choose PNG. Use both formats strategically to balance quality and performance.
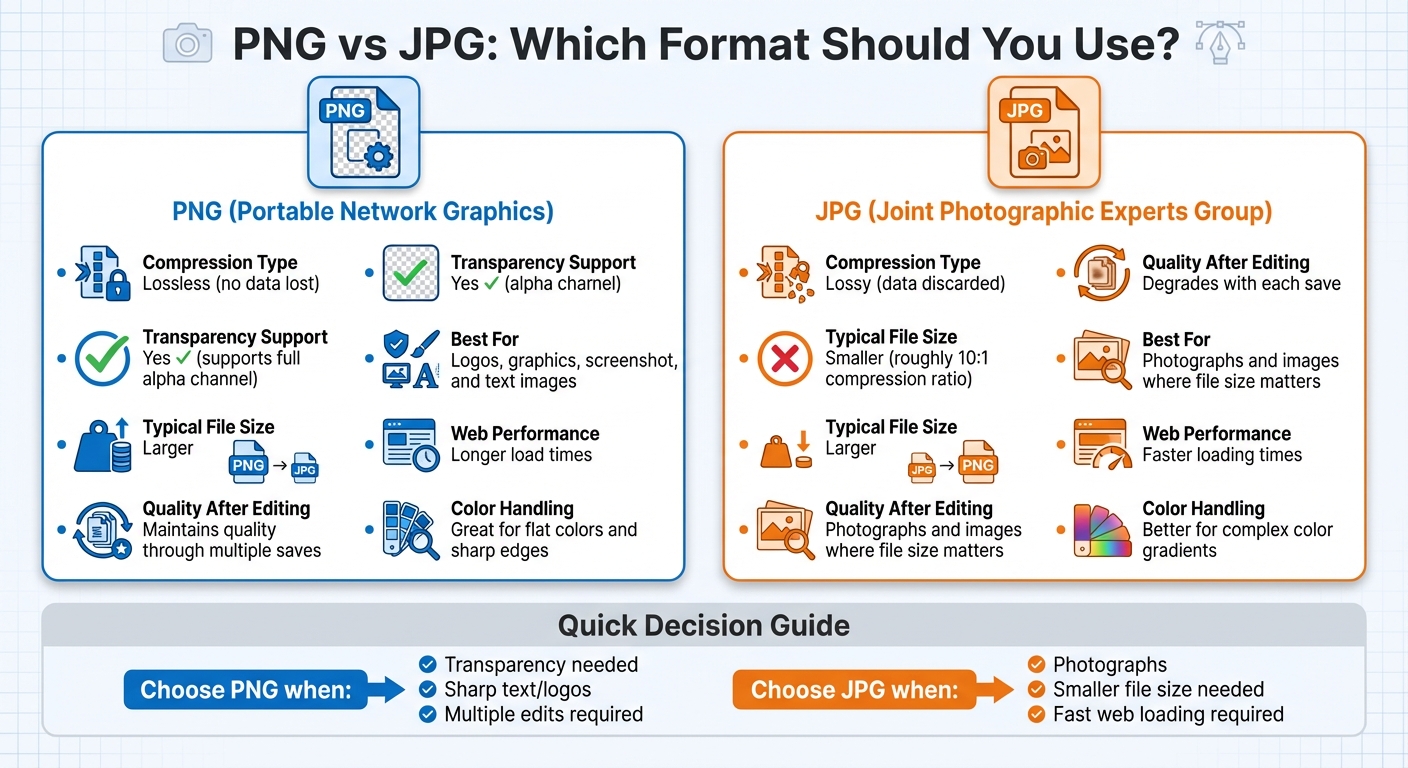
PNG vs JPG Format Comparison Chart
PNG Format: Features and When to Use It
Lossless Compression and Image Quality
PNG files use lossless compression, meaning every pixel is preserved, even after multiple edits. This type of compression is fully reversible, ensuring the image remains an exact match to the original file. Because of this, PNG is perfect for images that require sharp details and crisp text. It’s a go-to format when precision is non-negotiable. Additionally, PNG offers features that make it incredibly flexible for design work.
Transparency Support
One standout feature of PNG is its support for alpha transparency, which allows for smooth, graduated transparency levels. This makes it ideal for creating logos, icons, and user interface elements that need to blend seamlessly with different backgrounds. Whether it’s a subtle fade or a completely transparent section, PNG handles it effortlessly.
When to Use PNG
PNG shines in scenarios where clarity and detail are essential. Use it for screenshots, charts, infographics, or any design work requiring sharp text and fine details. Its ability to maintain consistent quality through repeated edits makes it a reliable choice for these applications.
JPG Format: Features and When to Use It
Lossy Compression and Quality Trade-Offs
JPG relies on lossy compression, a process that reduces file size by discarding non-essential data. This means details like minor color variations or background noise are removed, resulting in faster loading times and saving storage space. It’s a trade-off: you lose some image details, but the file becomes much smaller.
One of JPG's strengths is its adjustable compression. You can tweak the settings to find the right balance between quality and file size. For example, you might choose higher quality for important photos or crank up the compression for quick web uploads. This flexibility makes JPG great for detailed photographs, as it can handle millions of colors while keeping file sizes manageable.
No Transparency Support
Unlike formats like PNG, JPG does not support transparency. Any transparent or semi-transparent areas in your image will be replaced with a solid white background when saved as a JPG. This makes it a poor choice for logos, icons, or graphics that need to blend seamlessly into different backgrounds. If transparency is a must, PNG is the better option.
When to Use JPG
JPG shines in situations where small file sizes are a priority. It’s perfect for photography, social media posts, and image-heavy websites. Think email attachments, blog images, or any scenario where fast loading and low bandwidth are essential. Its compression efficiency makes it ideal for large photo galleries or optimizing web performance while maintaining decent visual quality.
Up next, we’ll compare PNG and JPG side by side to highlight their differences more clearly.
PNG vs JPG: Side-by-Side Comparison
Compression and Quality Differences
PNG relies on lossless compression, which means it retains every bit of detail in the image, no matter how many times you save it. On the other hand, JPG uses lossy compression, which sacrifices some data to reduce file size. This trade-off can lead to noticeable quality loss, especially if the image is saved multiple times.
File Size and Performance Impact
JPG's lossy compression is highly efficient, often achieving a compression ratio of 10:1. This results in smaller files that load quickly on websites, making them ideal for web use. PNG, however, keeps all the original data intact, which means much larger file sizes. While this ensures top-notch image quality, it also requires more storage and bandwidth. The table below highlights these distinctions.
Comparison Table
| Factor | PNG | JPG |
|---|---|---|
| Compression Type | Lossless (no data lost) | Lossy (data discarded) |
| Transparency Support | Yes, supports full alpha channel | No (does not support transparency) |
| Typical File Size | Larger | Smaller, roughly 10:1 compression ratio |
| Quality After Editing | Maintains quality through multiple saves | Degrades with each save |
| Best For | Logos, graphics, screenshots, and text images | Photographs and images where file size matters |
| Web Performance | Longer load times | Faster loading times |
| Color Handling | Great for flat colors and sharp edges | Better for complex color gradients |
sbb-itb-ba72479
How to Choose Between PNG and JPG
Format Selection Guidelines
The choice between PNG and JPG comes down to what matters most for your project - image quality or quick loading times. Go with JPG for photos and intricate images where smaller file sizes and faster load speeds are key. Opt for PNG when working with graphics that need sharp lines, vibrant colors, or transparency.
If you're dealing with images that require transparent backgrounds or will undergo multiple edits without losing quality, PNG is the better choice due to its lossless compression. For web content, a mix of both formats often works best - JPG for photos and PNG for graphics - to achieve a balance between visual appeal and performance.
Converting Between PNG and JPG with ConvertHub
Once you've decided on the right format, converting files is straightforward. ConvertHub makes it easy to switch between PNG and JPG formats. You can simply drag and drop files or paste a URL, and the tool supports over 800 file types. For added convenience, it allows batch processing, so you can convert multiple files at once.
ConvertHub offers free conversions for files up to 100 MB without requiring registration. For larger files - up to 2 GB - paid plans are available, which include priority processing. To ensure security, all conversions are protected with 256-bit encryption, and files are automatically deleted after processing.
Applying These Guidelines
With the right tools, you can optimize image performance effectively. Remember, nearly half of users abandon a website if it takes more than 3 seconds to load, and images account for 75–78% of a webpage's total weight. Whether you're working on web design, print projects, or content creation, ask yourself these key questions: Does the image need transparency? Is it a photo or a graphic? Will it require multiple edits? The answers will guide you to the best format for your needs every time.
What Is The Difference Between JPG & PNG Images? (Should You Use JPG or PNG?)
Conclusion
Deciding between PNG and JPG comes down to what you need from your images. JPG works best for photographs and detailed visuals where reducing file size matters more than preserving every detail. On the other hand, PNG is ideal for graphics, logos, or images that require transparency or need to withstand multiple edits without losing quality.
Think about your specific requirements: Does the image need transparency? Is it a photo or a graphic? Will it go through several rounds of editing? Answering these questions will help you make the right choice. Once you're clear, tools like ConvertHub can handle the conversion process seamlessly. It offers free conversions for files up to 100 MB and even supports batch processing for larger projects.
Whether you're designing a website, preparing print materials, or working on digital content, choosing the right format ensures your visuals look their best while meeting performance needs.
FAQs
When is it better to use PNG instead of JPG for your images?
You should go with PNG for images that need transparency, sharp edges, or fine details - like logos, icons, or graphics containing text. Thanks to lossless compression, PNG files maintain their quality, making them perfect for designs where precision and clarity matter.
In contrast, JPG works better for photographs or situations where reducing file size takes priority over retaining every detail. However, if your project involves web graphics with transparent backgrounds or layered designs, PNG is the smarter choice.
How can PNG's transparency feature improve my design projects?
PNG files come with a transparency feature that lets you create images with clear backgrounds. This makes it simple to layer them over different designs or colors without any awkward edges showing. It's a go-to choice for creating logos, icons, and graphics that need to fit smoothly into various layouts.
This transparency option helps you achieve a polished and professional appearance, offering flexibility whether you're designing for websites, presentations, or promotional materials.
What are the downsides of using lossy compression in JPG files?
When you save an image as a JPG, lossy compression kicks in to shrink the file size by discarding some image data. While this can save storage space and make sharing easier, it comes with a downside: a visible dip in quality. You might notice blurring, color shifts, or pesky artifacts, especially if the image has been compressed too much or edited multiple times.
If you're working on projects where every detail and color nuance matters - like professional photography or graphic design - JPG's lossy compression might not cut it. But for everyday moments, like sharing snapshots online or freeing up space on your device, JPG strikes a reasonable balance between quality and file size.