MP4 vs MOV vs AVI: Video Format Comparison Guide
When choosing a video format, your decision impacts file size, quality, and compatibility. MP4, MOV, and AVI are three of the most common formats, each designed for specific purposes:
- MP4: Ideal for streaming and sharing due to its small file size and universal compatibility. It balances quality and compression efficiently.
- MOV: Best for professional editing, especially on Apple devices. Offers higher quality but results in larger files.
- AVI: Focuses on preserving quality with minimal compression, making it suitable for archiving or TV production, though file sizes are significantly larger.
Quick Comparison
| Feature | MP4 | MOV | AVI |
|---|---|---|---|
| File Size | Small | Large | Very Large |
| Compression | High (Lossy) | Moderate | Low |
| Video Quality | Good | Very High | Highest (if uncompressed) |
| Compatibility | Universal | Apple-focused | Windows-focused |
| Best Use Case | Streaming, Social Media | Editing, Archiving | Archiving, TV Production |
Key takeaway: Use MP4 for everyday needs, MOV for editing, and AVI for maximum quality. The right choice depends on your goals - sharing, editing, or preserving.
MP4 vs MOV vs AVI Video Format Comparison Chart
1. MP4
Developer and Compatibility
MP4, formally known as MPEG-4 Part 14, is an international standard developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO/IEC). Unlike formats tied to specific companies, MP4 is universally compatible. It works effortlessly across platforms like Windows, macOS, iOS, and Android, as well as on smart TVs, game consoles, and nearly all web browsers. This broad support makes it a go-to format for most users.
Compression and File Size
MP4 employs lossy compression to shrink file sizes while maintaining high-quality playback. It relies on advanced codecs like H.264 and H.265, which focus on recording only the changes between video frames. This approach allows for efficient streaming - offering smooth playback of 1080p videos at roughly 8 Mbps or 4K videos at 35 to 45 Mbps without buffering issues.
Video Quality and Codec Support
What sets MP4 apart is its ability to maintain excellent video quality alongside its efficient compression. It supports widely-used codecs such as H.264 and H.265 (perfect for high-resolution content), MPEG-4, and AAC. Modern devices are equipped with hardware decoders for these codecs, which not only ensure smooth playback but also help conserve battery life. On the audio side, the AAC codec delivers better sound quality compared to older formats like MP3. Additionally, MP4 files can store metadata like titles, artist details, subtitles, and chapter markers, making it easier to manage media libraries.
Best Use Cases
MP4 is the top choice for streaming and social media platforms. Its ability to balance compression, quality, and compatibility makes it ideal for environments with limited bandwidth. For instance, TikTok imposes upload limits of 287.6 MB for mobile and 2 GB for web uploads. Thanks to its versatility, MP4 continues to be the preferred format for final video delivery.
2. MOV
Developer and Compatibility
MOV, officially known as the QuickTime File Format (QTFF), was developed by Apple Inc. and introduced in 1991. Initially designed as a proprietary format for QuickTime, it later became the foundation for the MPEG-4 (MP4) specification. MOV works seamlessly with macOS and iOS, making it a natural choice for Apple users. On Windows, however, playback often requires QuickTime Player or Windows Media Player. Since Apple ended official QuickTime support for Windows in 2016, many users have turned to third-party solutions like VLC. Similarly, Android users typically rely on apps like VLC for MOV playback. This platform-specific compatibility makes MOV particularly suited for professional editing workflows, especially in Apple ecosystems.
Compression and File Size
MOV prioritizes visual quality over compression efficiency. By using codecs like MPEG-4 or H.265 (HEVC), it ensures high-quality visuals, though this often results in larger file sizes. Its track-based architecture, which stores video, audio, and text as separate components, allows editors to modify individual tracks without altering the entire file. This flexibility is a significant advantage in professional editing environments.
Video Quality and Codec Support
MOV is widely recognized for delivering top-tier video quality. It supports a variety of codecs, from commonly used options like H.264 and H.265 to high-performance codecs such as Apple ProRes and ALAC. Its ability to handle detailed metadata and frame-accurate timecodes makes it a favorite for precise, pixel-perfect editing. While MOV can manage uncompressed video for the highest quality, most professionals prefer high-bitrate codecs to strike a balance between quality and storage needs.
Best Use Cases
MOV is a go-to format for video professionals, particularly in editing and post-production. As Adobe highlights:
"MOV files are one of the most common types of video production files. Whether you realize it or not, you probably use them most days".
The format shines in Mac-based workflows and is frequently used in editing tools like Final Cut Pro and Adobe Premiere. Its ability to handle separate media tracks and detailed metadata makes it ideal for complex editing tasks. MOV is also a solid choice for archiving master footage, where preserving maximum quality is critical. However, for distributing content - especially on social media or streaming platforms - converting MOV to MP4 is often a smarter option due to MP4’s better compression and wider compatibility.
3. AVI
Developer and Compatibility
AVI, short for Audio Video Interleave, was created by Microsoft and first introduced in November 1992 as part of its "Video for Windows" technology. According to MotionElements:
"Developed by Microsoft and introduced to the public in November 1992 as part of its Video for Windows technology, the AVI format is one of the oldest video formats."
Despite its age, AVI remains widely compatible across platforms, including Windows, macOS, Linux, Android, gaming consoles, and most web browsers. Adobe highlights this versatility:
"AVI (Audio Video Interleave) works with nearly every web browser on Windows, Mac, and Linux machines."
Unlike the more feature-rich MP4 and MOV formats, AVI sticks to a straightforward design focused on ensuring compatibility. This simplicity has helped AVI maintain its status as a reliable standard for storing audio and video files for decades. However, its basic, chunk-based structure lacks features like built-in subtitles or interactive menus.
Compression and File Size
AVI uses limited compression, which helps preserve high-quality audio and video but often results in larger file sizes. Its design allows for flexibility with codecs, meaning that two AVI files might appear identical but require different codecs to play properly.
Video Quality and Codec Support
AVI supports high-quality video and audio through a variety of codecs, with M-JPEG, DivX, and XviD being among the most commonly used. Its lighter approach to compression ensures that the video retains its fidelity and avoids noticeable artifacts.
Best Use Cases
AVI is best suited for situations where quality is prioritized over file size. It’s an excellent choice for archiving uncompressed master footage, as well as for TV production and DVD creation, where maintaining high-definition resolution and broadcast standards is critical. Legacy Windows editing systems also rely heavily on AVI. However, its large file sizes and lack of modern compression make it unsuitable for web streaming, social media uploads, or email sharing. In such cases, converting AVI files to MP4 is a more practical solution. These trade-offs highlight the balance between AVI's strengths and its limitations, offering a clear perspective on when this format is the right choice.
sbb-itb-ba72479
Video file formats explained - mov vs. avi vs. mp4 vs. flv vs. png vs.tiff
Strengths and Weaknesses
Each video format has its own set of perks and drawbacks, making it better suited for specific tasks. Knowing these differences can save you from the frustration of file conversion issues. Let’s break down the main strengths and weaknesses of MP4, MOV, and AVI formats to help you decide which fits your needs.
MP4 is the go-to choice for everyday use. Its high compression efficiency allows a 2-hour video to take up just 0.75 GB while keeping visual quality intact. However, this comes at a cost - MP4 uses lossy compression, meaning some original data is permanently removed to reduce file size. Thanks to its balance of quality and size, MP4 shines for streaming and mobile applications.
MOV is tailored for professional editing, especially on Mac systems where it integrates seamlessly with Final Cut Pro and other advanced editing tools. It supports features like timecodes and chapters, which are essential for editors. The trade-off? MOV files tend to be much larger than MP4s, making storage a consideration.
AVI prioritizes video fidelity by using minimal compression, making it perfect for archiving master files or producing TV content where quality is critical. Its superior quality stems from its low-compression approach. On the downside, AVI files are significantly larger, making them less practical for web streaming. Plus, they lack modern features like soft subtitles or interactive menus. Choosing AVI often boils down to whether quality outweighs file size for your project.
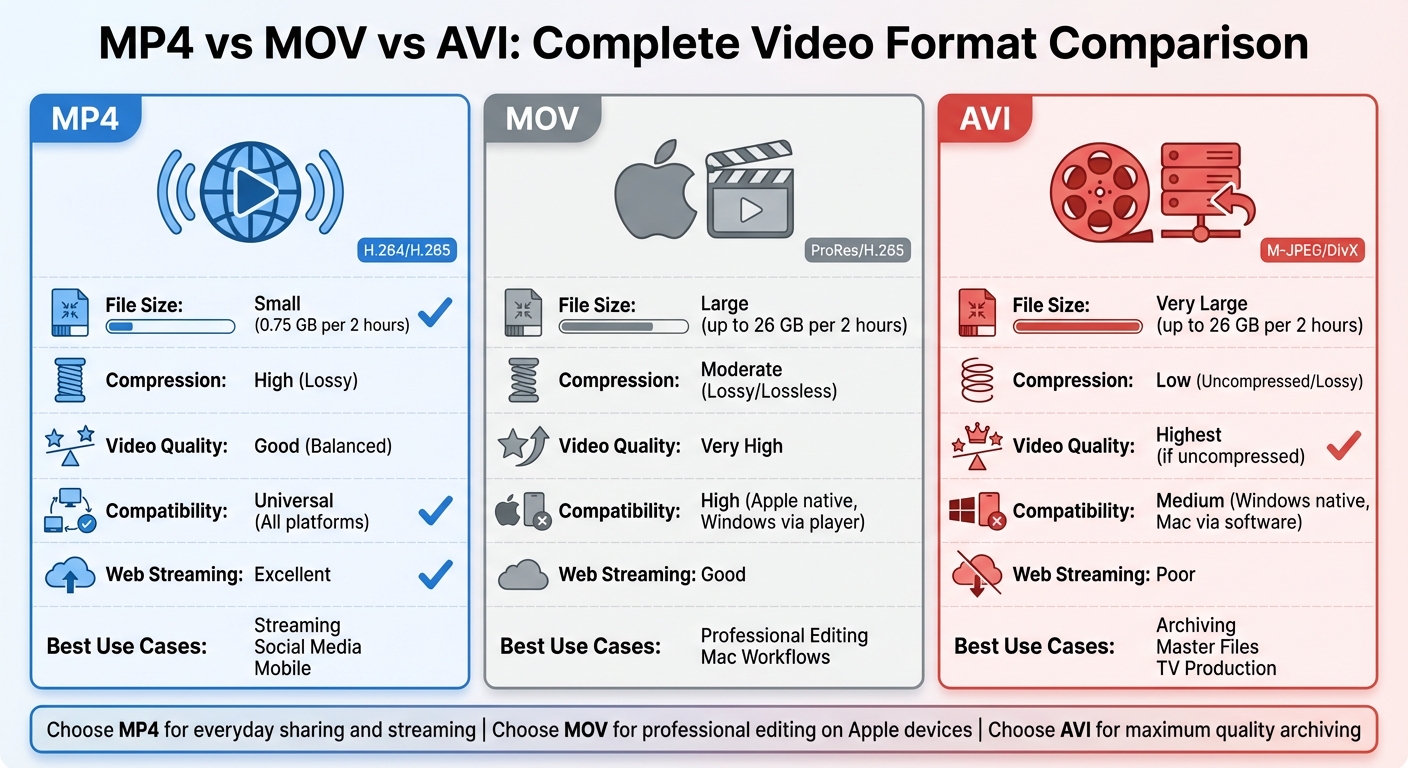
| Feature | MP4 | MOV | AVI |
|---|---|---|---|
| File Size | Small (0.75 GB per 2 hours) | Large (up to 26 GB per 2 hours) | Very Large (up to 26 GB per 2 hours) |
| Compression | High (Lossy) | Moderate (Lossy/Lossless) | Low (Uncompressed/Lossy) |
| Video Quality | Good (Balanced) | Very High | Highest (if uncompressed) |
| Device Compatibility | Universal (All platforms) | High (Apple native, Windows via player) | Medium (Windows native, Mac via software) |
| Web Streaming | Excellent | Good | Poor |
| Metadata Support | Subtitles, multiple audio, menus | Timecodes, chapters, effects | Limited (No native subtitles/menus) |
| Best For | Streaming, Social Media, Mobile | Professional Editing, Mac Workflows | Archiving, Master Files, TV Production |
Conclusion
Each video format shines in its own way, making the choice largely dependent on your specific workflow and requirements. MP4 stands out as the go-to option for everyday use. Its widespread compatibility, smaller file sizes, and suitability for streaming, social media, and mobile viewing make it a reliable choice for most users.
If you're working on professional video editing - especially on Apple systems - MOV is a better fit. This format retains more data during post-production, which is a big plus for tasks like color grading and applying effects. Just keep in mind that MOV files are typically much larger than MP4 files.
For those with specialized needs, AVI is worth considering. It’s particularly useful for archiving master files or working with older Windows systems. With minimal compression, AVI preserves the highest possible quality, but the large file sizes make it less practical for online sharing.
In short, MP4 is your all-around solution for most scenarios, MOV is ideal for high-quality editing on Apple platforms, and AVI is best for preserving top-tier quality when storage space isn’t an issue. The right format depends on your priorities and how you plan to use the video.
FAQs
What are the key differences in video quality between MP4, MOV, and AVI formats?
MP4, MOV, and AVI each handle compression and metadata differently, which directly impacts video quality and file size. MP4 is known for its efficient compression, keeping file sizes smaller without sacrificing much visual quality. This makes it a go-to format for streaming and everyday use. MOV, created by Apple, allows for lighter compression and supports a wider range of codecs. This makes it a favorite for professional editing and workflows that demand high-quality visuals and color accuracy. On the other hand, AVI, the oldest of the three, typically uses little to no compression. This results in exceptional raw image quality but comes with significantly larger file sizes, making it ideal for archiving or editing projects where preserving every detail is crucial.
What is the best video format for professional editing on a Windows PC?
When it comes to professional video editing on a Windows PC, AVI stands out as a top choice. This format provides uncompressed, high-quality video, making it perfect for projects where preserving the best possible video quality is a priority.
However, it's worth noting that AVI files can take up a lot of storage space because of their uncompressed nature. Make sure you have ample disk space available before diving into an editing project with this format.
How do MP4, MOV, and AVI compare in file size for a 2-hour video?
For a 2-hour video, MP4 is often the go-to format because it balances quality and file size. It keeps the file compact while maintaining good visual and audio quality, making it perfect for both storage and sharing. MOV files, while larger than MP4, deliver better quality, which makes them a favorite for professional video editing. Meanwhile, AVI creates the largest files since it uses minimal compression. This results in top-notch quality but demands a lot more storage space.